Impurities are substances inside a confined amount of Liquid, gas or solid, which differ from the Chemical Composition of the material or compound.
Impurities are either naturally occurring or added during synthesis of a chemical or commercial product. During production, impurities may be purposely, accidentally, inevitably, or incidentally added into the substance.
The level of impurities in a material is generally defined in relative terms. Standards have been established by various organizations that attempt to define the permitted levels of various impurities in a manufactured product. Strictly speaking, then, a material's level of purity can only be stated as being more or less pure than some other material.

| Sr. No. | Name of the compound | Structure of the compound | CAS Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Impurity A:(S)-N-(1-(isopentylamino)-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl)pyrazine-2-carboxamide | 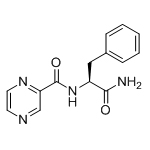 |
289472-80-6 |
| 2 | Impurity E: | anilide ).jpg) |
75706-12-6 |
| 3 | Impurity L:(S)-3-phenyl-2-(pyrazine-2-carboxamido) propanoic acid | 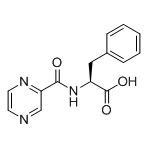 |
114457-94-2 |
| 4 | Impurity M:(S)-methyl 3-phenyl-2-(pyrazine-5-carboxamido)propanoate | 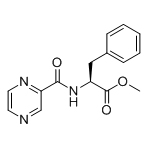 |
73058-37-4 |

| Sr. No. | Name of the compound | Structure of the compound | CAS Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4-(3-(4-Cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-2,4-dioxoimidazolidin-1-yl)-2-fluoro-N-methylbenzamide | phenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-2,4-dioxoimidazolidin-1-yl)-2-fluoro-N-methylbenzamide.jpg) |
1242137-18-3 |